Understanding Machine Vision: Applications, Challenges, and Future Innovations
What is Machine Vision?
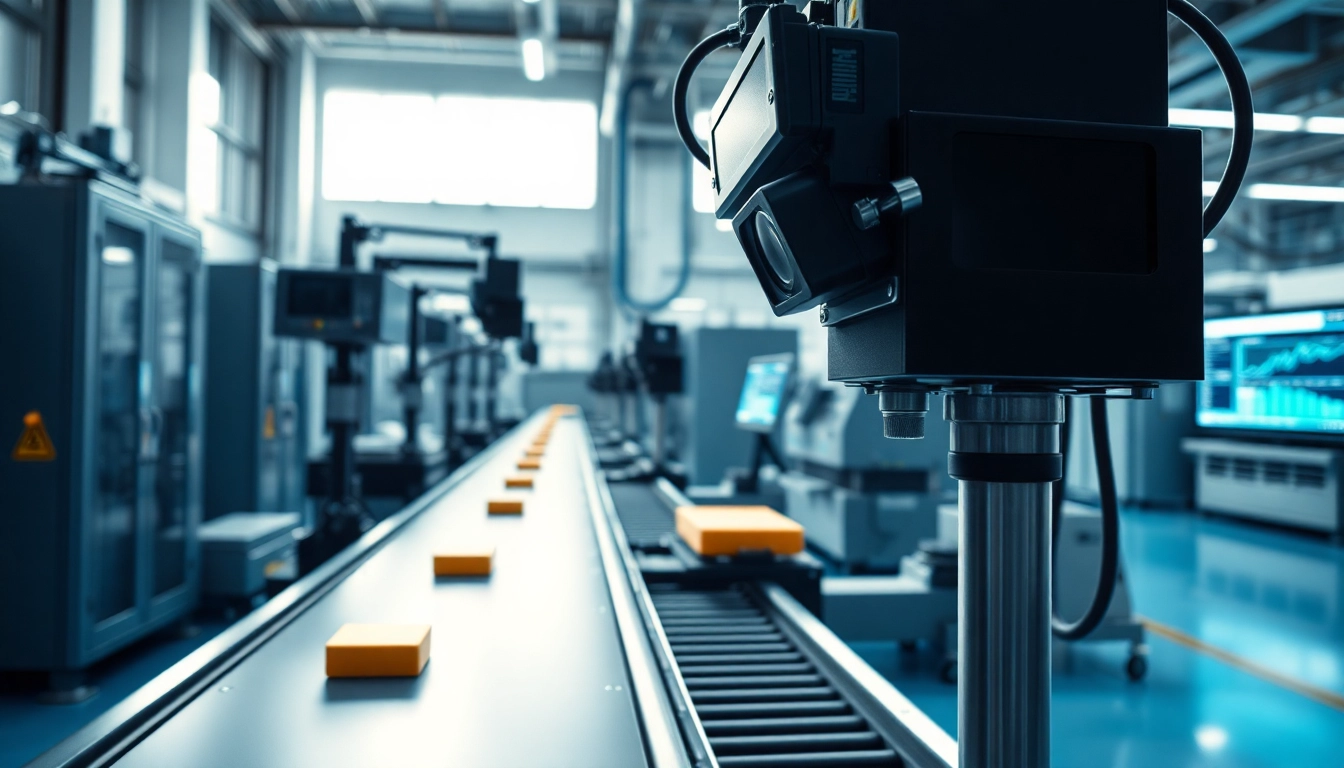
Machine vision is an innovative technology that allows computers and machines to interpret and process visual information in a manner similar to human sight. It combines cameras, sensors, and advanced algorithms to analyze images and automate tasks that require visual assessment. Industries across the globe are harnessing machine vision to improve efficiency, enhance product quality, and reduce operational costs.
Definition and Basic Principles
At its core, machine vision encompasses the ability to capture, process, and analyze images derived from various environments using optical systems. The fundamental principle involves capturing an image, processing that image, and making decisions based on the analyzed data. These systems operate through a series of steps, including image acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction, image analysis, and result interpretation. By employing high-resolution cameras and specialized lighting, these systems can discern minor defects, gauge dimensions accurately, and track the movement of objects, thereby enabling precise quality control across multiple applications.
Components of Machine Vision Systems
The effectiveness of a machine vision system hinges on its core components:
- Cameras: These are vital for capturing visual data. They come in various forms, including monochrome, color, and multi-spectral cameras, depending on the application.
- Lighting: Proper illumination is critical. Different lighting techniques, such as backlighting, diffuse lighting, and structured light, help enhance image quality and reveal essential details.
- Processing Hardware: This includes computers and processors that handle image data. The gear ranges from standard PCs to specialized processing units optimized for real-time analysis.
- Software: Algorithms and applications that interpret the captured images, perform necessary computations, and output actionable insights are crucial. Advanced software packages often integrate deep learning capabilities to improve accuracy and adaptability.
How Machine Vision Differs from Computer Vision
While machine vision and computer vision are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct purposes. Machine vision is primarily geared toward specific, deterministic tasks such as quality inspection, measurement, and identification in manufacturing settings. In contrast, computer vision encompasses broader topics, including image understanding, interpretation, and interaction in varied contexts, such as self-driving cars, image recognition, and augmented reality. Essentially, all machine vision falls under the umbrella of computer vision, but not all computer vision applications are machine vision.
Applications of Machine Vision
The utilization of machine vision spans a wide array of industries, transforming traditional practices into more efficient, accurate, and data-driven processes.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
In manufacturing, machine vision systems play a critical role in quality control processes. By employing sophisticated image analysis techniques, manufacturers can inspect products for defects, measure dimensions, and verify product consistency in real-time. For instance, companies can implement machine vision systems to ensure that components meet exact specifications, enabling them to catch defects before products reach the customer. Automated quality inspection not only speeds up the production line but also significantly lessens the likelihood of human error, thereby ensuring a higher quality product.
Automated Inspection Processes
Machine vision streamlines various automated inspection processes. Systems equipped with advanced optical character recognition (OCR) can automatically check labels and packaging for accuracy, while barcode scanners can ensure optimal logistics and inventory management. Moreover, in environments demanding high levels of cleanliness, such as the pharmaceutical and food industries, machine vision can inspect for contaminants or foreign objects in products, thereby safeguarding consumer health.
Machine Vision in Robotics and AI
Integrating machine vision into robotics and AI enhances the capabilities of automated systems. Robots equipped with vision systems can navigate complex environments, interact with objects, and perform tasks requiring dexterity and precision. For example, in warehouse settings, vision capabilities enable robots to identify and categorize items, optimizing supply chain management. The use of AI in conjunction with machine vision technologies allows for continuous learning, where systems adapt to new scenarios and improve their performance over time, making automation even more intelligent and efficient.
Benefits of Implementing Machine Vision
The integration of machine vision technologies not only elevates operational efficiencies but also provides significant advantages across various domains.
Cost Efficiency and Productivity Boost
One of the most compelling benefits of implementing machine vision is the notable boost in productivity it offers. By automating visual tasks, companies can reduce labor costs, speed up production cycles, and minimize downtime related to inspections and quality checks. Investments in machine vision can lead to shorter returns on investment as businesses experience lower operational costs while maintaining or improving outputs.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability
Machine vision systems significantly outshine human capabilities regarding accuracy and consistency in inspections. They eliminate subjective interpretations that can lead to errors and variations in quality assessments. This reliability in output ensures that companies can adhere to quality standards and regulations without excessive scrutiny or rework, ultimately fostering a more robust reputation in their respective markets.
Real-Time Data Integration and Processing
The ability to process and analyze data in real-time is another major advantage. This capability allows companies to monitor production lines continuously, respond swiftly to anomalies, and make instant adjustments to maintain quality and efficiency. Real-time insights also foster better decision-making, as companies can track trends and performance metrics to stay ahead of potential issues.
Challenges in Machine Vision Implementation
Despite its advantages, adopting machine vision technology presents several challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure successful implementation.
Technical Limitations and Errors
Machine vision systems can experience technical challenges, including issues related to lighting, camera resolution, and environmental factors that affect image quality. Incorrect setups may lead to misinterpretations or errors in detecting defects during inspections. To mitigate these challenges, organizations should invest in comprehensive training for their technical teams and carry out thorough testing and calibration of the systems prior to deployment.
Cost of System Setup and Maintenance
The initial investment and ongoing maintenance of machine vision systems can be significant. Companies must budget for high-quality cameras, processing equipment, and specialized software. Moreover, as technology evolves, continuous upgrades and maintenance may be necessary to retain optimal functionality. Organizations should conduct a cost-benefit analysis to ensure that the long-term gains from using machine vision outweigh the setup and maintenance costs.
Training and Skill Requirements for Operators
Effective use of machine vision technology requires skilled operators who can interpret data and troubleshoot issues. The learning curve can be steep, particularly for organizations that have not previously integrated such technologies. This necessitates investment in training programs to upskill current employees or hiring new talent with appropriate expertise in vision system management.
Future Trends in Machine Vision Technology
The future of machine vision technology is set to be transformative, with rapid advancements and the integration of cutting-edge innovations.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
As machine learning algorithms continue to evolve, the integration of AI with machine vision will enable systems to learn from experience and improve accuracy autonomously. This evolution will lead to adaptive inspection processes, where systems can adjust to new product lines, configurations, and environmental changes without requiring extensive reprogramming. Using AI will also empower machine vision systems to handle increasingly complex visual tasks, enhancing capabilities in quality control, predictive maintenance, and anomaly detection.
Advancements in Imaging Technology
The development of new imaging technologies, such as hyperspectral imaging and advanced sensors, will further extend the capabilities of machine vision systems. These advancements will allow for the detection of material composition and finer details that are currently beyond the reach of conventional imaging techniques. In addition, improved camera technology will facilitate higher resolutions and faster processing speeds, thereby augmenting the operational efficiency of machine vision applications.
Potential for Industry-Specific Solutions
As industries continue to identify unique challenges and requirements, there will be a growing demand for customized machine vision solutions. Whether in automotive manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, or logistics, tailored systems will address specific demands across various sectors. This trend will push companies to develop niche products that cater to particular operational challenges, leading to further innovation and specialization in the machine vision space.