Mastering Infusion Resins for Advanced Composite Production
Understanding Infusion Resins
Infusion resins are critical components in modern composite manufacturing, offering a blend of performance, flexibility, and innovation. These resins are designed to optimize the vacuum infusion process, making them particularly effective for creating lightweight, high-strength composites utilized across various industries. The significance of infusion resins cannot be understated, as they provide the backbone for advanced applications in aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction sectors.
What Are Infusion Resins?
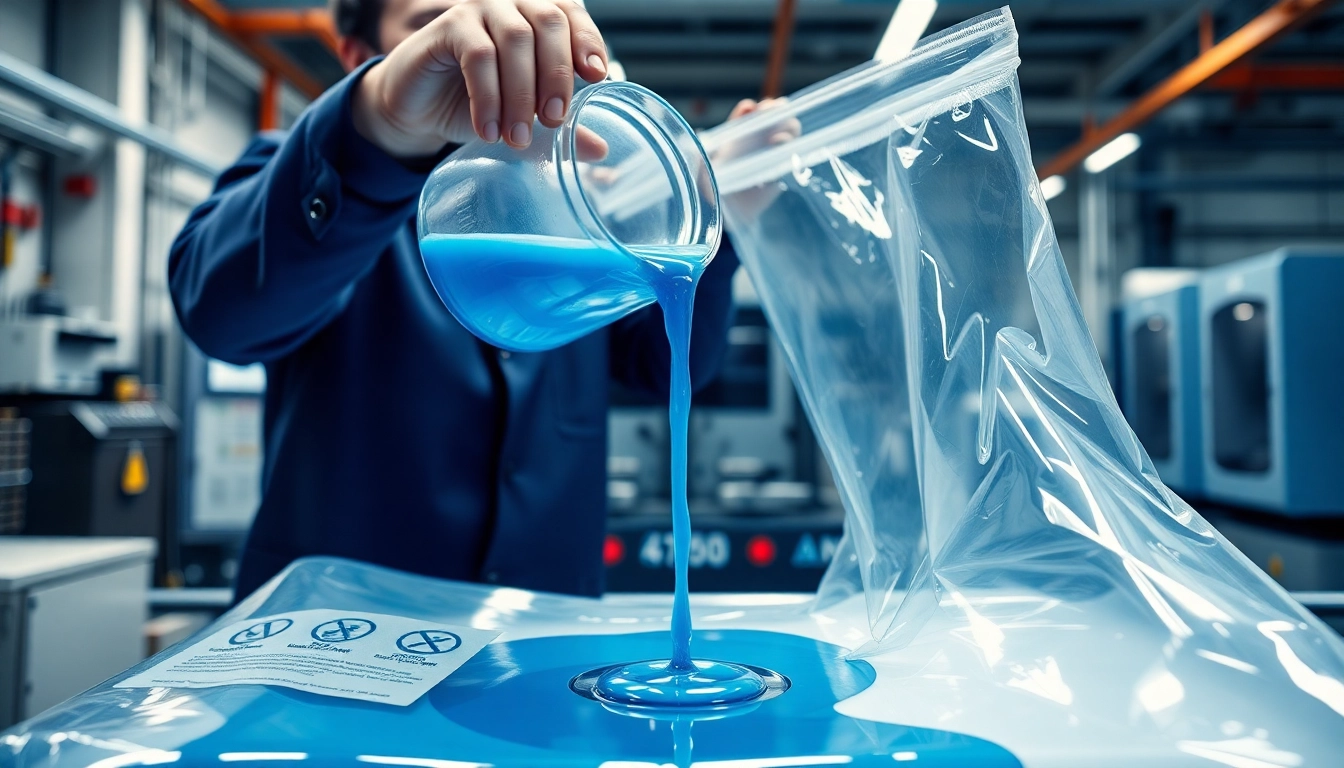
Infusion resins are low-viscosity polymers tailored for the vacuum infusion process, a methodology where resin is drawn into a dry fiber preform under vacuum conditions. This technique reduces void content, enhances mechanical properties, and allows for better fiber wetting compared to traditional methods like hand layup. Infusion resins typically exhibit properties such as low viscosity, improved flow characteristics, and heightened strength, making them ideal for complex geometries and large-scale parts.
Key Properties and Benefits of Infusion Resins
Infusion resins offer several advantages over conventional resin systems:
- Low Viscosity: This characteristic allows the resin to flow easily through the fiber mat, ensuring comprehensive saturation and minimal air entrapment.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Infusion resins contribute to lightweight structures without compromising strength, essential for applications where performance is critical.
- Enhanced Clarity: Many infusion resins provide optical clarity, beneficial in applications where aesthetics are as important as functionality.
- Controlled Curing Times: Tailored pot life and curing times allow for flexibility during application, depending on the complexity of the mold and ambient conditions.
- Thermal and Chemical Resistance: Depending on the formulation, infusion resins can withstand harsh environments, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Popular Applications in Industries
Infusion resins have a diverse range of applications, including:
- Aerospace: Used in the manufacture of primary and secondary structures, infusion resins ensure weight savings and superior mechanical performance in aircraft.
- Automotive: Lightweight composite parts, such as body panels and structural components, rely on infusion resins for durability and performance.
- Marine: Boat hulls and components benefit from infusion resins, providing strength while reducing weight for better fuel efficiency and handling.
- Construction: In infrastructure projects, infusion resins are utilized to create composite materials that offer both aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
The Process of Resin Infusion
The resin infusion process is critical to achieving high-quality composite materials. A thorough understanding of each step ensures optimal results and strengthens the final product’s integrity.
Step-by-Step Guide to Infusion Process
The resin infusion process can be broken down into the following stages:
- Preparation: The mold and fibrous substrate (like carbon or glass fiber) are prepared, and release agents are applied to facilitate easy demolding.
- Layering: Dry fibrous materials are strategically layered within the mold to create the desired composite structure.
- Vacuum Setup: Once the dry fibers are placed in the mold, a vacuum is applied to remove air, which helps prevent voids during the infusion.
- Resin Injection: The resin is injected into the mold, filling the dry fiber preform. The vacuum pressure allows for even resin distribution.
- Curing: After the resin has been introduced, it is allowed to cure under controlled conditions until it hardens completely.
- Demolding: Once cured, the composite part is demolded and prepared for any additional processing or finishing.
Equipment Needed for Successful Infusion
Essential equipment for resin infusion includes:
- Mold: A high-quality mold made from materials such as aluminum or silicone.
- Vacuum Pump: Used to create the necessary vacuum to remove air from the system.
- Flow Media: Helps distribute the resin through the fiber composite evenly.
- Resin Reservoir: A container to hold the infusion resin prior to injection.
- Piping and Fittings: To connect the resin reservoir to the mold and facilitate smooth resin flow.
Best Practices for Optimal Results
To achieve the best results during the resin infusion process, consider the following best practices:
- Temperature Control: Maintain the optimal temperature for resin saturation and curing to prevent premature hardening or flow issues.
- Vacuum Integrity: Regularly check to ensure the vacuum setup is airtight to prevent leaks or air entrapment.
- Monitoring Flow Rate: Control the resin flow rate to avoid rapid infusion that may lead to uneven saturation.
- Post-Processing: After demolding, perform necessary finishing steps to enhance the material properties and appearance of the composite.
Choosing the Right Infusion Resins
Selecting the appropriate infusion resin is essential for achieving desired performance characteristics in composite materials. Various factors influence this decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Infusion Resins
When choosing infusion resins, consider:
- Viscosity: Choose resins that match the flow requirements based on the complexity of your mold design.
- Curing Time: Select resins that align with your production timeline and environmental conditions.
- Mechanical Properties: Evaluate tensile strength, elasticity, and thermal resistance to meet application needs.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the sustainability of the resin formulation and whether it meets industry environmental standards.
Comparing Different Types of Infusion Resins
Infusion resins may vary significantly in performance characteristics. Here are key comparisons:
| Resin Type | Viscosity | Mechanical Properties | Curing Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | Low | High strength and stiffness | Room temperature or heat-assisted |
| Vinyl Ester | Medium | Good chemical resistance | Room temperature |
| Polyester | High | Cost-effective but lower strength | Room temperature |
How to Test and Validate Your Resin Selection
Testing is vital when selecting infusion resins to confirm they meet project specifications:
- Sample Testing: Create test samples using your selected resin and analyze mechanical properties post-curing.
- Environmental Testing: Subject samples to environmental conditions mimicking end-use applications for performance assessment.
- Feedback Analysis: Gather data from prototype applications and make informed modifications based on results.
Common Challenges with Infusion Resins
Despite their advantages, using infusion resins can present challenges. Identifying these problems early can save time and resources.
Identifying Common Mistakes in Infusion Processes
Common mistakes during the resin infusion process include:
- Poor Mold Preparation: Inadequate surface preparation can lead to adhesion issues and improper curing.
- Inconsistent Vacuum Levels: Fluctuations in vacuum pressure can create voids and weaken composite integrity.
- Incorrect Resin Mixture: Failing to measure resin and hardener accurately can result in improper curing.
How to Troubleshoot Infusion Resin Issues
Troubleshooting strategies for resin infusion issues include:
- Conduct a Retrospective: Review the infusion process and isolate variables that may have contributed to failure.
- Experiment with Variables: Adjust resin viscosity or infusion speed and monitor effects on final product quality.
- Seek Expert Advice: Collaborate with industry experts to gain insights into advanced troubleshooting methods.
Case Studies of Successful Problem Resolution
Several companies have effectively resolved infusion challenges:
One case involved an aerospace manufacturer who faced issues with air entrapment during the infusion process. After conducting a thorough analysis, they implemented a more advanced vacuum system and adjusted the resin’s viscosity, leading to significantly improved part integrity and performance. Similar case studies illustrate that systematic troubleshooting and experimentation can lead to positive outcomes.
Future of Infusion Resins in Composite Manufacturing
The landscape of infusion resins is likely to evolve continuously as manufacturers strive for innovation and sustainability in composite production.
Innovations in Infusion Resin Technology
Emerging technologies in infusion resins include:
- Smart Resins: These resins could incorporate sensors that monitor curing conditions and mechanical properties in real time, allowing for adjustments during the manufacturing process.
- Bio-Based Resins: Innovations in bio-resin formulations are being explored for more sustainable manufacturing options without sacrificing performance.
- Advanced Catalysts: New curing systems promise to enhance curing rates and performance, expanding the applications of infusion resins in various industries.
The Role of Sustainability in Resin Development
As industries become increasingly environmentally conscious, sustainability in resin development is paramount. Manufacturers are focusing on bio-based materials and recyclable resin systems, reducing carbon footprints while maintaining performance standards. The future of infusion resins will likely prioritize sustainable practices, ensuring they align with global environmental goals.
Predictions for Industry Trends in the Coming Years
Looking ahead, several trends are anticipated in the infusion resin industry:
- Increased Demand: As composite usage rises across various sectors, so will the demand for robust infusion resins.
- Technological Advancements: Continued research into material science will yield improved resin formulations that cater to specific industrial needs.
- Greater Focus on Circular Economy: Infusion resins will increasingly be expected to fit within circular economy principles, emphasizing recyclability and reduction of waste.