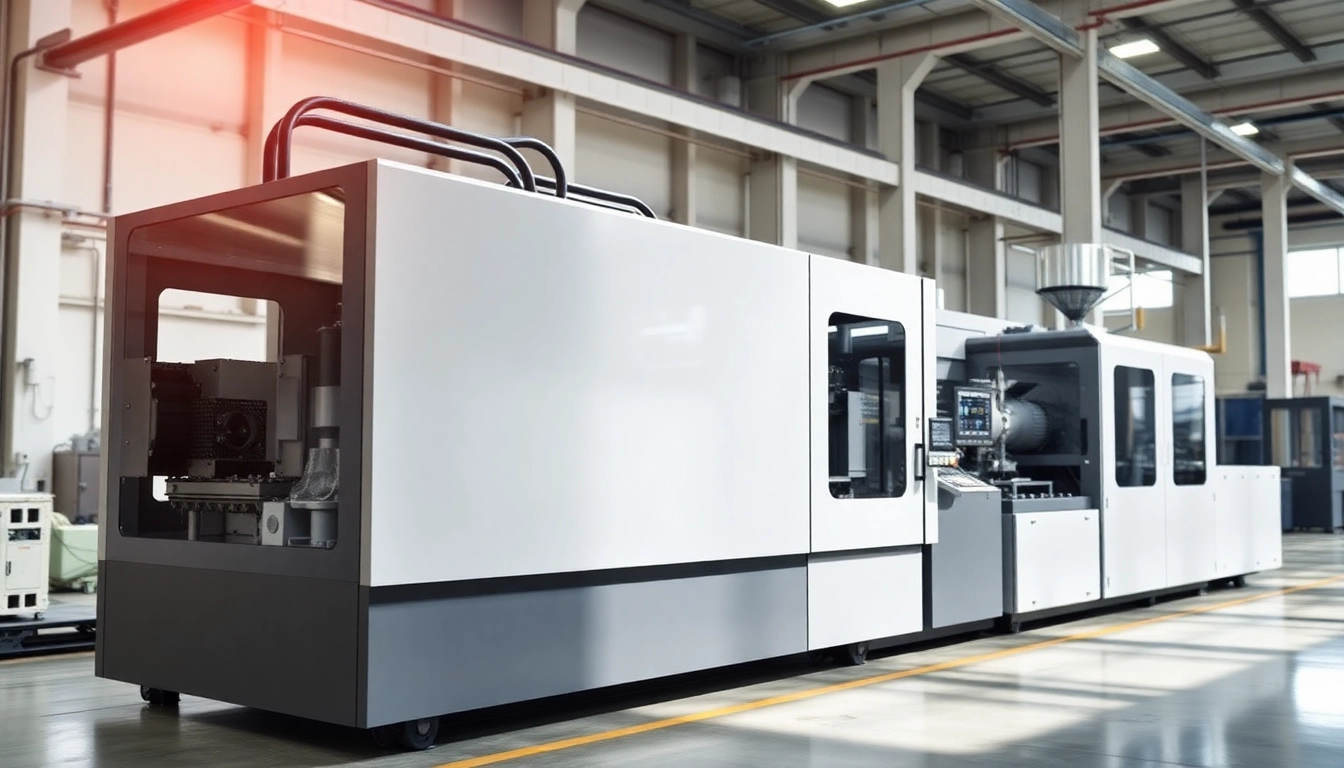
Boost Your Production with Advanced Blow Molding Machines for Every Need
Understanding Blow Molding Machines
What is a Blow Molding Machine?
A blow molding machine is a device used in manufacturing hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers, through a process that involves inflating a heated plastic parison within a mold. The principle behind blow molding relies on creating a hollow piece using compressed air. This technique offers several advantages, including uniform wall thickness, production efficiency, and the ability to create complex shapes. Notably, the process can also minimize waste, as any excess can often be reprocessed. For manufacturers looking to enhance their production capabilities, investing in a high-quality Blow Molding Machine is essential.
Types of Blow Molding Processes
Blow molding encompasses three primary types: Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM), Injection Blow Molding (IBM), and Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM). Each method serves different applications and offers unique advantages:
- Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM): This process begins with melting plastic and extruding it into a parison, which is then inflated within a mold. EBM is well-suited for high-volume production of containers and is often favored for its speed and efficiency. It’s commonly used in making large bottles and containers.
- Injection Blow Molding (IBM): This technique combines injection and blow molding to create precise and intricate shapes. Initially, a preform is injection molded, and once it’s cooled, it’s heated again and blown into its final shape. This method is ideal for small, precise parts, such as pharmaceutical bottles.
- Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM): This process is a variation of the IBM that includes stretching the preform while blowing it into shape, resulting in stronger bottles with higher clarity and barrier properties, which is critical in packaging sensitive products.
Applications of Blow Molding Machines
Blow molding machines find extensive applications across various industries:
- Packaging Industry: The packaging industry is perhaps the most significant user of blow molding technology, producing bottles for beverages, chemicals, and household products.
- Automotive Industry: Blow molding is used for creating parts such as fuel tanks, air ducts, and other interior components, where the lightweight and durable properties of molded plastics are advantageous.
- Consumer Goods: From toys to storage containers, the versatility of blow molding allows for a broad range of designs and functionalities in consumer products.
- Medical Equipment: Blow molding is often used to manufacture medical devices and packaging due to the precision and cleanliness of the process, ensuring quality control for sensitive applications.
Choosing the Right Blow Molding Machine
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a blow molding machine, various features should be evaluated to ensure it aligns with production goals:
- Machine Type: Choose between EBM, IBM, and ISBM depending on the end product requirements.
- Production Speed: Assess how quickly the machine can produce items, as higher speeds may significantly enhance throughput.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for machines that consume less power to reduce operational costs significantly.
- Automation Level: Fully automated machines can streamline operations, while semi-automatic options offer a balance of control and speed.
- Mold Changeover Ease: Consider how quickly and easily the machine can be adjusted for different productions, as this can affect overall efficiency.
Comparing Manual vs. Automatic Machines
Understanding the differences between manual and automatic blow molding machines is crucial for making an informed decision:
- Manual Machines: These machines require more operator involvement and are better suited for low-volume productions or experimental setups. While they are generally less expensive, they can lead to inconsistencies in quality and output.
- Automatic Machines: These can operate with minimal human intervention, leading to higher consistency and efficiency. Automatic machines are ideal for large-scale production, though they usually come with higher upfront costs.
Cost Analysis of Blow Molding Machines
The cost of blow molding machines can vary widely based on features, size, and technology. Here’s a breakdown of key cost considerations:
- Initial Investment: Basic models may start at $2,000, while advanced automatic machines can exceed $100,000. Consider the scale and complexity of the products you aim to produce.
- Operational Costs: Factor in energy consumption, maintenance, and labor costs when calculating overall operational expenses. High energy efficiency can significantly reduce these costs.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Evaluate potential ROI by analyzing production capacity, waste reduction, and demand projection for your products.
Best Practices for Operating Blow Molding Machines
Setup and Calibration Techniques
Proper setup and calibration are critical for achieving high-quality results with blow molding machines. Here are best practices:
- Initial Calibration: Ensure the machine settings—temperature, pressure, and speed—are optimized for the material and product size.
- Regular Checks: Frequent monitoring of machine parameters helps in promptly identifying deviations and adjusting accordingly.
- Mold Inspection: Regularly inspect molds for wear and tear. Any issues can significantly affect quality and production rates.
Maintenance Routines for Longevity
Adopting a comprehensive maintenance routine will extend the lifespan of the blow molding machine:
- Daily Maintenance: Conduct routine checks on hydraulic fluids, lubrication, and electrical components to ensure everything is functioning correctly.
- Weekly Inspections: Examine molds, mechanical parts, and calibration settings at least once a week to prevent potential breakdowns.
- Professional Servicing: Engage professionals for in-depth maintenance and repairs to tackle complex issues that may arise.
Safety Guidelines for Operators
Safety should be prioritized in the operation of blow molding machines. Here are essential guidelines:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Operators should always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and ear protection.
- Emergency Procedures: Familiarize all operators with emergency shutdown procedures to mitigate risk during an anomaly.
- Training Programs: Regular training sessions should be conducted for all operators to ensure they are equipped with the latest safety practices.
Common Challenges in Blow Molding
Understanding Production Defects
Identifying and addressing production defects is vital for maintaining product quality. Common defects include:
- Non-uniform Wall Thickness: Often caused by variations in heating and cooling; ensuring even heat distribution can help mitigate this defect.
- Surface Defects: Such as splay or bubbles, which can occur due to moisture in the material or improper processing temperatures.
- Dimensional Inaccuracies: Regularly calibrating the machine and ensuring consistent material input can substantially reduce such issues.
Efficiency Optimizations
Improving efficiency in blow molding operations can lead to significant cost savings:
- Material Selection: Choosing appropriate materials can reduce waste and improve the durability of the final product.
- Cycle Time Reduction: Analyze and optimize the cycle times for different products to enhance throughput.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems: Implementing real-time monitoring systems can detect inefficiencies and allow for timely adjustments.
Adapting to Market Demands
Staying adaptable to market changes is crucial for success:
- Trend Analysis: Keep an eye on market trends and customer preferences to inform production strategies.
- Product Diversification: Investing in versatile blow molding machines can allow manufacturers to pivot quickly to produce in-demand products.
- Feedback Loops: Establishing systems for obtaining and acting on customer feedback ensures products remain relevant.
Future Trends in Blow Molding Technology
Revolutionary Materials and Processes
The future of blow molding technology is bright, with innovations leading to improved capabilities:
- Biodegradable Materials: The shift towards sustainable practices is pushing the use of biodegradable plastics, reducing environmental impact.
- Advanced Resins: New types of resins can improve the performance and adaptability of blow-molded products, enhancing their market viability.
- Smart Technology: The integration of IoT devices in blow molding machinery allows for enhanced monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
As industries embrace digital transformation, blow molding is no exception:
- Automated Control Systems: Autonomous control systems can significantly reduce errors and optimize production runs.
- 3D Printing and Prototyping: Allowing for rapid prototyping can accelerate the development of new products and improve customizations.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging analytics for performance monitoring can provide actionable insights on machine operation and product quality.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
Environmental concerns are influencing the evolution of blow molding technology:
- Recycling Initiatives: Many manufacturers are integrating recycled materials into their processes, lowering dependency on virgin plastics.
- Energy-Efficient Designs: New blow molding machines are designed to consume less energy, thus reducing the carbon footprint.
- Waste Reduction Technologies: Innovations aimed at minimizing waste during production cycles are becoming increasingly mainstream.