Essential Steps for Effective Facade Installation in Modern Construction
Understanding Facade Installation
What is Facade Installation?
Facade installation refers to the process of attaching and constructing the exterior facade of a building. This critical component not only influences the architectural aesthetics of the structure but also plays an essential role in its functionality and energy efficiency. The facade serves as a protective layer against environmental elements while contributing to the overall thermal performance and energy usage of the building. In addition to protecting the interior, a well-designed facade can enhance the visual appeal, making it a significant aspect of modern architecture. Understanding facade installation is crucial for architects and builders alike, as it involves various materials, installation techniques, and compliance with local building codes.
The Importance of Facades in Architecture
Facades play a pivotal role in defining a building’s character and integrating it within its environment. They are often the first aspect of a building that is perceived by visitors, making their design crucial in conveying the building’s purpose, style, and quality. In urban settings, facades contribute to the visual continuity and cultural identity of neighborhoods. Moreover, innovative facade designs can enhance energy efficiency by utilizing natural light, promoting ventilation, and incorporating insulation materials that reduce heating and cooling needs.
Types of Facade Systems
Facade systems can be categorized into several types based on the materials used and the construction techniques involved:
- Unitized Facades: Prefabricated panels that are assembled off-site and installed in sections.
- Stick-built Systems: These are built in place using distinct framing components and can provide adaptability for complex shapes.
- rainscreen systems: Designed for moisture management, these systems allow for drainage and ventilation between the cladding and the building’s core.
- Glazed Facades: Comprising glass elements that allow for natural light penetration, enhancing the interior ambiance.
- Metal Cladding: Utilized for durability and aesthetic purposes, often applied in commercial and industrial buildings.
Key Materials Used in Facade Installation
Common Materials and Their Properties
Facade installation employs a variety of materials, each chosen for their unique properties and roles in the overall facade system:
- Brick: Known for its durability and aesthetic variety, brick provides excellent thermal mass and a classic appearance.
- Stone: Offering natural beauty and durability, stone facades require careful installation to manage weight and structural integrity.
- Wood: Sourced from sustainable practices, wood can be visually warm but requires proper treatment to resist decay and pests.
- Concrete: A versatile and robust option, concrete can be manipulated into various forms and finishes, providing both structural strengths.
- Glass: Vital for modern designs, glass facades allow light penetration while creating a sense of openness.
- Metal: Such as aluminum or zinc, metal options are lightweight, strong, and can be finished in numerous colors and textures.
Choosing the Right Adhesives and Fasteners
The choice of adhesives and fasteners is critical to the success of facade installation. Mechanical fasteners, adhesives, or a combination of both are typically employed to secure the facade to the structural frame.
Mechanical fasteners include screws, bolts, and anchors that provide immediate load support, while adhesive options can enhance connections, particularly for glass and lightweight materials. The selection depends on factors such as load requirements, environmental conditions, and compatibility with the curtain wall or other facade systems in use.
Innovative Materials in Facade Design
With advancements in technology, innovative materials have emerged that enhance both performance and sustainability in facade design:
- Photovoltaic Panels: These panels integrated into facades generate electricity, contributing to energy savings.
- Responsive Materials: Such as self-cleaning coatings that respond to environmental conditions, reducing maintenance needs.
- Green Facades: Incorporating vegetation for insulation and aesthetic appeal while improving air quality.
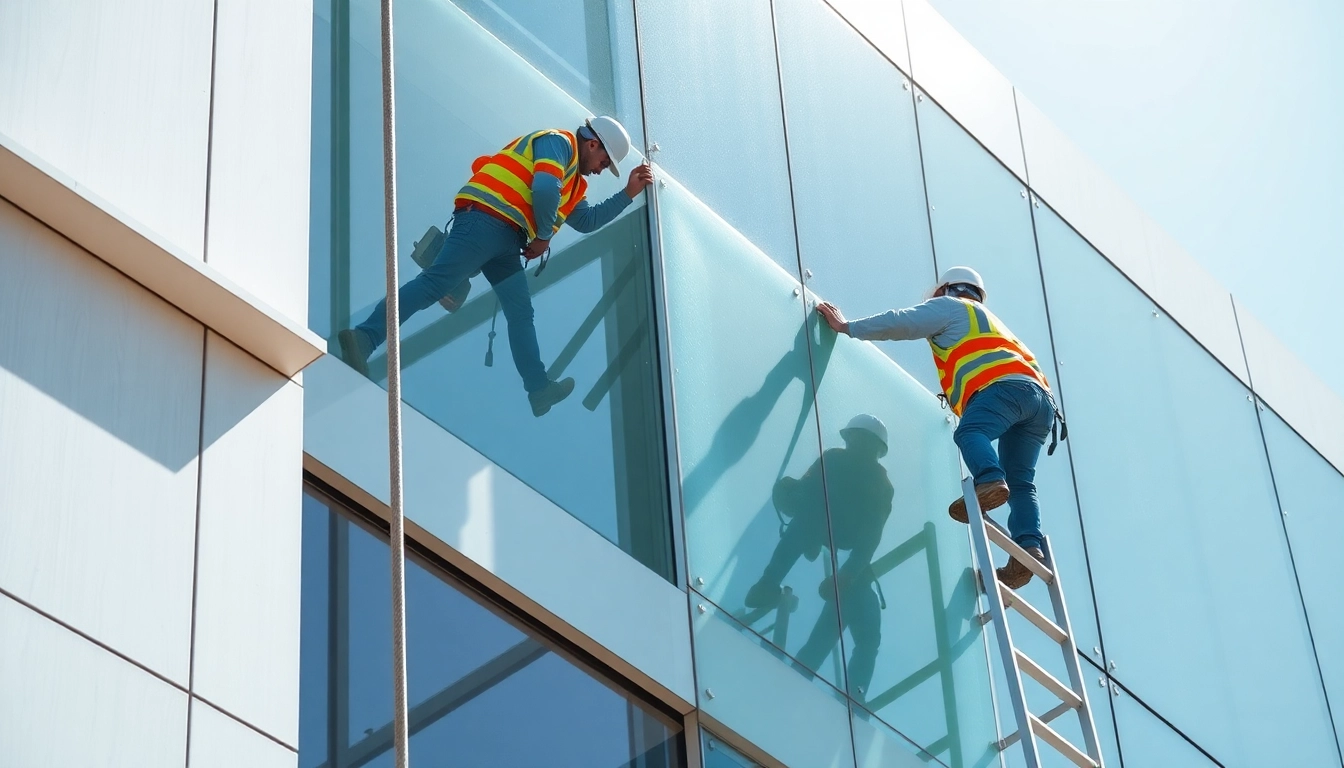
Step-by-Step Process of Facade Installation
Preparation and Inspections
The preparation stage is crucial in establishing a solid foundation for facade installation. Key tasks include:
- Site Assessment: Conducting surveys to evaluate existing conditions, including structural integrity and site-specific factors affecting installation.
- Material Preparation: Ensuring all chosen materials comply with design specifications and are ready for installation.
- Safety Inspections: Checking equipment and scaffolding to uphold safety standards during installation.
Installation Techniques and Methods
Installing a facade involves a systematic approach, frequently employing the following techniques:
- Leveling and Alignment: Ensuring that each section is correctly level and aligned before securing it in place.
- Sequential Installation: Working methodically from a designated starting point, often the bottom up, to ensure proper drainage and prevent moisture accumulation.
- Integration of Utilities: Incorporating electrical, water, and HVAC elements within the facade, requiring careful coordination with other trades.
Post-Installation Quality Checks
Once the installation is complete, a series of quality checks must be conducted to ensure that the facade meets design standards:
- Thermal Imaging: Assessing for proper insulation and thermal performance.
- Water Tightness Testing: Ensuring that no water penetrates through the facade.
- Visual Inspection: Examining the aesthetic finish and alignment of facade elements.
Advanced Techniques in Facade Installation
Facades on High-Rise Buildings
Implementing facade systems on high-rise buildings presents unique challenges that require specialized approaches. Key considerations include:
- Access and Safety: Utilizing cranes and hoisting techniques to transport materials safely to higher elevations.
- Structural Analysis: Understanding wind loads and seismic considerations to ensure the facade system can withstand external forces.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Modern facade designs increasingly prioritize energy efficiency, employing strategies such as:
- High-Performance Glazing: Selecting glass with low U-Values to reduce heat loss.
- Insulation Materials: Incorporating advanced insulation materials that minimize energy usage.
- Shading Devices: Designing overhangs or vertical fins to minimize solar heat gain during peak sunlight hours.
Incorporating Technology in Facade Design
Integration of smart technologies into facade systems has become more prevalent, enabling buildings to adapt to their environments. Examples include:
- Dynamic Facades: Systems that adjust based on sunlight exposure, enhancing energy management.
- Building Management Systems (BMS): Monitoring performance and optimizing facade conditions in real-time for comfort and efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions in Facade Installation
Common Challenges Faced During Installation
Facade installation poses several challenges that require foreseen planning and agility to address:
- Weather Dependencies: Adverse weather conditions can delay installation timelines, necessitating contingency planning.
- Material Compatibility: Different materials may require specific adhesives or fasteners, leading to delays if not pre-verified.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all materials and methods comply with local building codes can pose additional hurdles.
Best Practices for Overcoming Issues
To mitigate these challenges, implementing best practices is essential:
- Thorough Planning: Involving all stakeholders in planning and coordination from the outset.
- Flexible Timelines: Allowing buffer periods in project timelines to manage unexpected delays.
- Regular Training: Ensuring that the installation team is updated on new materials and techniques.
Case Studies of Successful Facade Installation Projects
Analyzing successful facade installations can provide valuable insights and lessons learned. For instance, the 30 St Mary Axe (“The Gherkin”) in London showcases a glass facade system that responds to changing weather conditions while maximizing natural light. This project involved meticulous design and execution, demonstrating high-performance standards in both aesthetics and functionality.
Another noteworthy example is the One World Trade Center in New York. The installation of its advanced glass facade required precise engineering to manage the building’s unique shape and height, resulting in a stunning façade that is both functional and iconic.
In reflection, the facade installation process is an intricate blend of art and engineering that requires an understanding of materials, techniques, and best practices. By navigating through the complexities of facade systems, architects, and builders can create stunning, efficient, and sustainable structures that not only stand the test of time but also contribute positively to their environments.